Anabolic reaction - Reaction that constructs or synthesizes molecules from smaller units usually requiring input of energy ATP in the process. BIOA322 Describe the role of ATP in biochemical reactions.
Atp Cycle Structure And Role Of Atp In Biological Reactions Study Score
How are energy requirements different in our two examples and why.

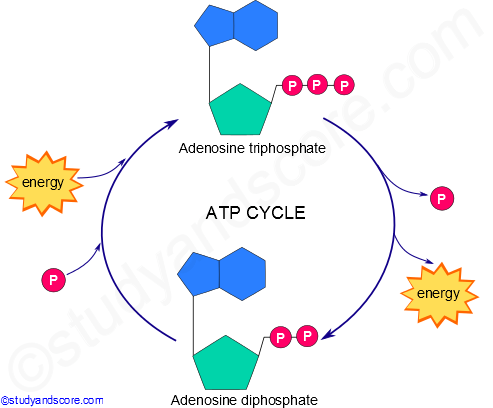
. Identify the role of ATP as an intermediate between catabolism and anabolism. ATP and GTP are primary sources of energy for biochemical reactions. Pushing of endergonic reactions that would not occur spontaneously ATP transfers a PO 4 group to a reactant Reactant can now react more easily with other molecules New chem bonds forms o Transport work.
In a coupled reaction ATP is first used to store energy from a catabolic reaction and then used to release energy for an anabolic reaction. The cells then break down ATP releasing energy as they engage in a variety of activities explain Drs. Entropy S is a measure of disorder.
Explain what are redox reactions and why they are important Explain the activation energy and its role in biochemical reactions Describe the role of ATP and activated electron carriers Explain what are biological catalysts and why they are important for life Explain how enzymes catalyse biochemical reactions Explain what are ribozymes. 2 points maximum Adenosine 3 phosphates or guanosine 3 phosphates. Catabolism-breaking down reactions-energy is released and then harvested to synthesize ATP anabolism Anabolism-building reactions-Biosynthesis-stored energy is used to build complex molecules They are coupled together Via ATP cycle.
To be able to define energy work power their units so. Elaborating on the phosphate bonds eg. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed.
Cells extract energy from foods through a series of reactions that have negative free energy changes. Metabolic role of ATP is that the nucleoside triphosphate acts as the energy store or as the energy currency of the cell. BIOA321 Compare and contrast the basic transformation of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Also called HEAT CONTENT. BIOA311 Describe the fundamental roles of plastids eg chloroplasts and mitochondria in energy transformations. Introduction - Enzyme Characteristics.
Here is a cute animation on how cell respiration and photosynthesis are related. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism particularly in energy transfer within cells. BIOA322 Describe the role of ATP in biochemical reactions.
Pumping of substances across membranes against the direction of. So the answer to your question is. BIOA311 Describe the fundamental roles of plastids eg chloroplasts and mitochondria in energy transformations.
Formation of bonds with ATP cleavage. The forming of ATP which is an endergonic process and is related to proton gradient dissipation is an example. Name and describe the role of any cofactors.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 4th Quarter Weeks 1-5 Explain coupled reaction processes and describe the role of ATP in energy coupling and transfer Explain the importance of chlorophyll and other pigments Describe the patterns of electron flow through light reaction events Describe the significant events of the Calvin cycle Differentiate aerobic from anaerobic respiration Explain. Browse course material library_books arrow_forward. Catabolism is energy forming ADPP -- ATP so in catabolis ATP is the product.
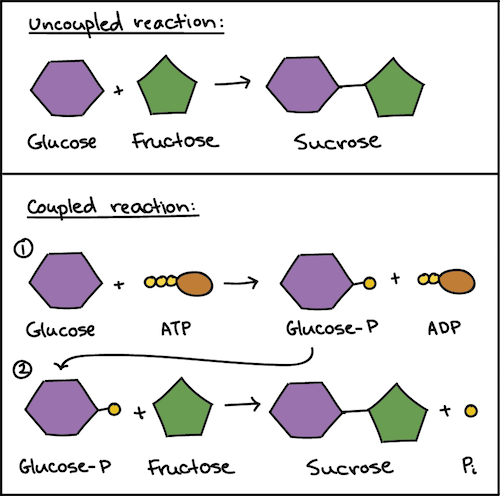
Coupled reactions are described as reactions that are joined together and are used to push the second reaction with the release of free energy in one reaction. Show activity on this post. The ATP molecule have three high energy phosphate groups and that molecule is used to transfer one of its phosphate groups to fructose-6-phosphate and also provide energy to carry out the reaction.
Role of Enzymes in Biochemical Reactions. So the role of 80 p is to is for its hydraulics ISS to provide free energy to make otherwise non spontaneous processes be spontaneous and to occur. BIOA322 Describe the role of ATP in biochemical reactions.
What other reactions of. By modeling the function of ATP in an inquiry lab you can accurately identify the various levels of cellular work done by Adenosine TriphosphateStandardsBIOA311 Describe the fundamental roles of plastids eg chloroplasts and mitochondria in energy transformationsBIOA321 Compare and contrast the basic transformation of energy. 2 What type of chemical reaction is involved in the conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate.
ATP provides energy for the transport of sodium and potassium by way of a membrane-embedded protein called the sodium-potassium pump NaK pump. In other cases they are firmly bound together by covalent bonds. Is energy storing ATP -- ADP P in anabolism ATP starts the reaction.
Describe the role of the ATP in coupling exergonic and endergonic reactions in a cell. Think intensity duration. The second reaction is then driven by the hydrolysis breakdown of ATP which releases energy.
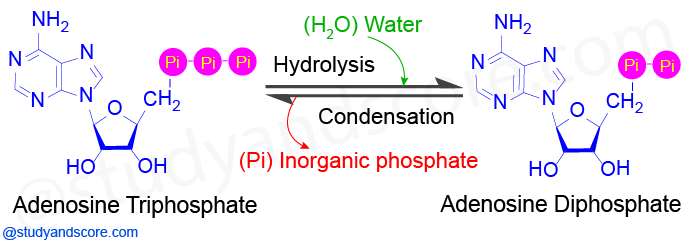
1 Define and briefly explain the role of entropy and enthalpy in biochemical reactions Enthalpy H is the change in chemical bond energy in a reaction bond energy of products minus the bond energy of reactants. In essence your cells extract the chemical energy from various nutrient molecules like proteins carbohydrates and proteins and use the chemical energy to make ATP. Another use of ATP is phosphorylation of.
The following passages from the book by Darnell Lodish and Baltimore I are typical. Catabolic reaction - Reaction that releases energy as complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones. You will go together with the free energy change for another reaction involving phosphate to produce a spontaneous reaction.
Where do we get our energy from. What does this energy allow us to do. Activate the protein by changing its geometric shape or by actually participating in the overall reaction.
Biochemical Reactions Enzymes and ATP Biochemical Reactions Enzymes and ATP. ATP is a relatively small molecule that serves as an energy intermediate in human metabolism. A Describe the structure of the ATP or the GTP molecule.
Sum of all chemical reactions within a living organism. Activation Energy - The amount of thermal energy that must be absorbed by. Enzymes are catalysts that boost the reaction rate.
Its energetically unfavorable to move sodium out of or potassium into a typical cell because this movement is against the concentration gradients of the ions. The activating role of a cofactor is to either. It is often negligible in reactions ATP hydrolysis in which the.
Atp Cycle And Reaction Coupling Energy Article Khan Academy
Atp Cycle Structure And Role Of Atp In Biological Reactions Study Score

Emma Wilson Uk Blogger On Instagram With One Week To Go Until Teaching Recommences I Am Going Over Summary Notes From The Biology Module Of La Kalligrafiya
0 Comments